





How To Use The Program



Our goal is to help you understand your conditionand how to keep yourself as healthy as possible.
If you have any questions please ask your doctoror healthcare provider.
Please remember to turn your volume up on thecomputer because some slides have sound.
Some slides will open in a separate window.Remember to come back to this presentation byclosing the window.
Welcome


After reviewing this material, you should be able to:
Describe the importance of monitoring your blood sugar
Tell what your blood sugar and A1C should be
Recognize the symptoms of low and high blood sugar
Identify the proper treatment of low and high blood sugar
Describe the importance of foot care and exercise
Explain the importance of planning meals
Describe the importance of diabetes medication
Important Things To Know


What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a life-long condition.
There is no cure for this disease, but it ispossible to live a healthy life with propercare.
You will need to learn the skills necessary tocontrol diabetes because uncontrolleddiabetes can lead to serious long termcomplications.


What Is Diabetes?
Does not make ANY insulin.
Does not make ENOUGHinsulin.
Or the muscle cells in thebody do not use the insulinwell (this is called insulinresistance).
Insulin is a hormone thathelps to lower blood sugar.
Diabetes is a life-long disease in which the pancreas either:


What Are The Risk FactorsFor Developing Diabetes?
•Family history of diabetes
•Age greater than 45years
•Overweight
•Lack of physical activity
•Smoking
•History of vasculardisease
•Race/ethnicity
•History of GestationalDiabetes
•Hypertension (equal to orgreater than 140/90mmHg)
•High cholesterol/hightriglycerides


What Are The DifferentKinds Of Diabetes?
There are 4 categories of diabetes:
1.Pre-diabetes
2.Type 2
3.Type 1
4.Gestational Diabetes


What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
•The pancreas may not make enough insulin.
•The pancreas may make enough insulin but the bodyisn't able to use it.
•Type 2 diabetes may be related to hereditary causes.
•Type 2 diabetes is usually diagnosed in adulthood, butmay occur in children and teenagers who are overweight.
•Type 2 diabetes is more common than Type 1.


What Is Type 1 Diabetes?
•In Type 1 diabetes there is little or no insulin beingmade by the pancreas.
•Type 1 diabetes may be an autoimmune disease.
•It usually occurs in children or young people andmay occur in older adults.
•Most people with Type 1 diabetes will need to takeinsulin for the rest of their lives.


What Is Blood Glucose?
Blood glucose or blood sugar isthe amount of sugar in theblood. Most of the time it iscalled “blood sugar”.
When food is eaten it is brokendown into a sugar calledglucose.
Glucose is needed for energy.


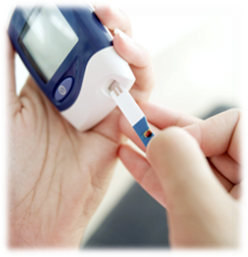
What Should My Blood SugarLevel Be?
If you did not have diabetes, your fasting blood sugar should be in the rangeof 70 – 99mg/dl. You are encouraged to check your blood sugar at home.You will need to discuss your target blood sugar range with your doctor andeducator.
It is important to keep the blood sugar glucose as close to the target aspossible.
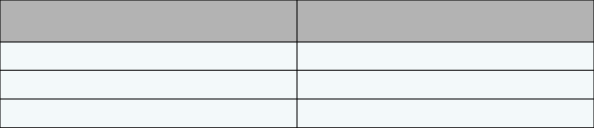
Timing of Test
American Diabetes Association
Fasting blood sugar
70 – 130mg/dl
2 hours after start of meal
Less than 180mg/dl
Bedtime blood sugar
110 – 150mg/dl



Why Is It Important To Know YourA1C Value?
The A1C reading measures the average blood sugar overthree months. The higher the blood sugar, the higher theA1C.
The goal is to keep an A1C reading under 7%; under 6.5 %is even better.
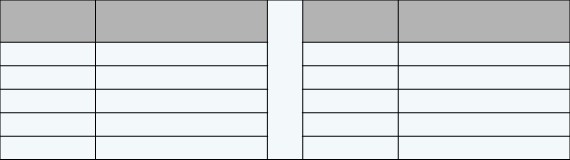
A1C %
Average Blood sugar
A1C %
Average Blood sugar
4%
60 mg/dl
9%
240 mg/dl
5%
100 mg/dl
10%
275 mg/dl
6%
135 mg/dl
11%
310 mg/dl
7%
170 mg/dl
12%
345 mg/dl
8%
205 mg/dl
13%
380 mg/dl


Why Is Blood Sugar Monitoring So Important?
Monitoring allows you to see how eating, exercise,and medications affect your blood sugar.
High and low blood sugars can cause seriousproblems, so you need to be aware of them.
If you don’t check your blood sugar,
you don’t know what it is.





Test Your Knowledge
Why is monitoring your blood sugarimportant ?


How Often and When ShouldBlood Sugar be Checked?
You will need to check as often as ittakes to gain understanding andcontrol of your diabetes.
Patients on insulin or diabetes pillsmay need to check several times aday.
As you take control of your diabetes,you and the team can decide the bestmonitoring schedule for you.
Suggested times to check are:
•Fasting (first thing in the morning, beforeyou eat)
•Two hours from the start of the meal
•Bedtime
•During illness, stress, or just feelingbadly


What Is A Low Blood Sugar(Hypoglycemia)?
In general, any blood sugarreading lower than 70 mg/dlis too low.
If you take insulin or pills,you are more likely to havea low blood sugar.
•Too little food
•Skipping or delaying a meal
•Too much diabetes medicine
•Being more active than usual
•Drinking alcohol
What causes low bloodsugar?


Low Blood Sugar Symptoms











Fast heart beat
Shaky
Sweaty
Anxious
Hungry
Dizzy
Weak
Headache
Blurry vision
Irritable




What Do You Do If You AreHaving A Low Blood Sugar?
Step 1. Check your blood sugar
Step 2. Eat or drink some type of carbohydrate
•Regular soda, juice, hard candy, or glucose tablets
•Do not use chocolate or candy bar to treat low blood sugar
Step 3. Wait 15 minutes
Step 4. Recheck your blood sugar


Preventing Low Blood Sugar
Eat meals on time.
Follow your meal plan.
Eat a little extra foodbefore exercising, ifneeded.
Take your diabetesmedicine as directedby your doctor.
Always Be Prepared:
Carry some type ofcarbohydrate or sugarwith you.
Wear an identificationbracelet or necklace.


Test Your Knowledge
What can you treat a
low blood sugar with?


What Is High Blood Sugar(Hyperglycemia)?
Hyperglycemia or high bloodsugar is defined as blood sugarlevels higher than your target.
What causes high bloodsugar?
•Not taking your medication asdirected
•Eating too much food orcarbohydrate
•Not enough exercise
•Having a cold or infection
•Stress
•Some medications
Hyperglycemia often
starts slowly
May lead to a medicalemergency if not treated



High Blood Sugar Symptoms









Thirsty
Urinating often
Hungry
Dizzy
Slow healing
Dry, itchy skin
Very tired
Headache
Blurry vision



What To Do if YourBlood Sugar is Too High
Step 1. Check your blood sugar every 4 hours
Step 2. Drink plenty of fluids that do not have sugar
Step 3. Call your doctor if:
•Vomiting more than once
•Unable to eat for more than 24 hours
•Diarrhea 5 or more times OR longer than 24 hours
•Breathing is difficult
•Blood sugar levels are higher than 300mg/dl two times in arow
•Urine ketones measure moderate to large


Sick Days
“Sick” may mean:
Fever
Vomiting
Nausea
Diarrhea
Head or chest congestion
If you are sick, it is vital thatyou watch for the followingsymptoms of high bloodsugar:
Nausea/vomiting
Severe dehydration
Increased urination
Weakness
Increased thirst


Sick Day Guidelines
ALWAYS take your medication, unless told not to by your doctor.
CHECK your blood sugar every 2 – 4 hours.
CHECK your ketones & notify your doctor, if moderate to large.
DRINK at least 8 ounces of diet and caffeine-free fluids every hour whileawake.
KEEP a log and record this information.


If You Are Unable to Eat
If your blood sugar is more than 250mg/dL before your meal
Continue to drink diet, caffeine-free fluids for that meal
If your blood sugar is between 180 – 250mg/dL
Eat or drink one carbohydrate serving for that meal
Continue to drink the diet, caffeine-free fluids
If your blood sugar is less than 180mg/dL
Eat or drink the number of carbohydrate servings in your meal plan
Continue to drink the diet, caffeine-free fluids


What About Exercise?
Exercise can be an effective toolfor lowering blood sugar.
Before starting an exerciseprogram make sure your healthcare provider says it is safe foryou to participate in a regularexercise routine.



Foot Care
High blood sugar damages theblood vessels and nerves in yourfeet.
•Wash your feet every day.
•Look at the top and bottom ofeach foot every day.
•Wear shoes ALL the time evenplaces that you might normallygo barefoot.
•Wear socks or stockings.
If you notice any signs or symptoms ofinfection see your doctor!!
Do not ignore these warning signs!A small problem can rapidly
become a BIG one!


Signs And SymptomsOf Infection
•Difficulty walking
•Warmness to the touch
•Swelling of feet and legs
•Drainage or pus from wound
•Persistent pain in feet and legs
•Redness
•Fever and chills


Role of Diet In ControllingBlood Sugar
Food raises blood sugar.
What, when, and how much you eat directlyaffects your blood sugar level.
The more you understand about food, thebetter you will be able to manage yourdiabetes.



Spacing and Timing of Meals
DO NOT skip meals.
Eat breakfast!
Eat at least three times throughout the day.
Eat meals around the same time each day.
Try to eat the same amount of carbohydrate at each meal.
Learn to balance your meal times with your medicine.


What Are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates (carbs) are a source of energy for your bodyand it is very important to include them in your diet and notavoid them.
Carbohydrates are any food that turns to sugar (starches,breads, sweets, fruit, and milk).
Beverages that contain fruit or sugar, such as juice andregular soda.
Ask your dietitian how many carbs you should have at eachmeal.


Here Are Some Examples OfONE Serving Of Carbohydrate:
1 small orange or apple 1/3 cup cooked rice or pasta
½ large banana ½ small baked potato
2 Tbsp dried fruit ½ cup mashed potatoes
1 cup of melon or berries 1 cup mixed vegetables
½ cup fruit juice or canned fruit ½ cup peas, corn
1 slice of bread or small roll ½ cup beans (kidney, pinto, lima, etc.)
1 corn tortilla (6” across) 1 cup 1% or non-fat milk
½ hamburger bun 1 cup light yogurt
½ small bagel or English muffin ½ cup frozen yogurt
1 small pancake (4” across) 4-5 crackers
¾ cup unsweetened dry cereal 3 cups low fat popcorn
½ cup cooked cereal baked potato chips (15-20)
1 Tbsp syrup, jam, jelly, honey 2 Tbsp light syrup



The Plate Method For Diabetes Meal Planning
Fruit
Milk
Non-starchyVegetable
Meat orOtherProtein
BreadStarchGrain


See Your Dietitian aboutSpecific Diet Requirements

Call to make an appointment
910-715-1925 or (800)-364-0499


What About Diabetes Medications?
You may need diabetes medicines if meal planning and exercise do notkeep your blood sugars controlled. Some people may take one ormore diabetes pills. Some people may need to take pills and/or insulinto keep their blood sugars controlled. No matter what type ofmedication that you may need for diabetes control, there are severalimportant things that you should know:
The name of your diabetes medicine(s)
The best time to take your diabetes medicine(s)
It is also very important to make sure you take the right amount of yourmedication
Notify your primary health care provider if you are having any major side effectsor concerns with your medicines.


Test Your Knowledge
What should you know about yourdiabetes medication?






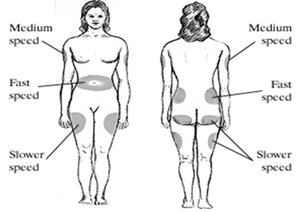
Where Do I Give My Insulin Shots?
Knowing where on your body youshould give your shots is veryimportant. You should choose adifferent area within the area for eachshot. This is called site rotation. Alwaysremember to avoid giving insulin shotsin areas that are bruised, lumpy or hasa scar from having had surgery.
The sites to use are:
•Abdomen (do not use within a 2-inch circle around the navel)
•Upper arm
•Anterior and lateral aspects of thethigh
•Buttocks
The pictures below show the
best locations




Thank You !




Correct


Try Again


